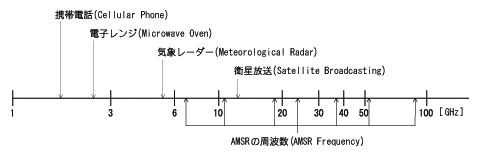
Fig. 1.1.1 Microwaves in familiar applications, and AMSR frequencies |
The Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer (AMSR) mounted on satellites is a passive sensor that measures weak microwaves radiated from the Earth at several frequencies. Microwaves contribute to improving our lives through their use in familiar applications, such as cellular phones, microwave oven, meteorological radar, and satellite broadcasts. Furthermore, the frequencies used in AMSR are close to those used in these devices. Microwaves are radiated naturally from the Earthfs atmosphere, land, and seas. The amount of energy radiated varies depending on the frequency, so physical quantities of water can be extracted by combining data at several frequencies. Typical physical quantities that can be extracted from the AMSR are cumulative water vapor content, cumulative cloud and water volume, rainfall for the atmosphere, snow depth and soil moisture volume for land areas, sea-ice distribution for iced areas, sea surface temperature, and wind speed on the sea.
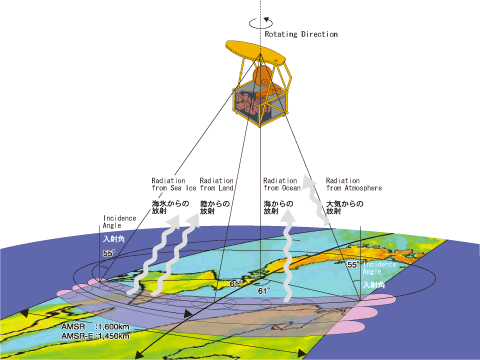
Fig. 1.1.2 Overview of observation by passive microwave radiometer |